End-point Communication
网络上的End-point communication需要保证以下几个方面:
(1)Confidentiality: secret
(2) Authetication
(3) Integrity: 消息确实来自某人以及not tampered
而网络攻击者可能会进行以下攻击:
(1) 读message
(2) 修改message
1. Confidentiality: Cryptography
Cryptography就是:
plaintext ----Encryption Algorithm + key---> ciphertext
(nothing more than mathematical operations)
KB(KA(m)) = m
KA(m): ciphertext encrypted using KA
1.1 symmetric key systems
Ripley’s and Zijun’s keys are identical and secret.
Example
DES
AES
1.2 public key systems
A pair of keys is used. The public key is known to both Ripley and Zijun (Actually, known to the whole world.).
The private key is only known to either Zijun or Ripley.
Example
RSA
包含两个部分:
(1) choice of public key and private key,
(2) encryption and dectryption algorithm
concerns about public-key cryptography
(1)任何人可以宣称自己是Ripley然后向Zijun发送message.
----> 怎么办? Solution: Digital Signature (绑定sender和message)
(2) time-consuming (DES is at least 100 times faster than RSA in hardware.)
----> 怎么办? Solution: Combination with symmetric key cryptography
2. Integrity: Hash Function
Two Methods to ensure message integrity
To ensure message integrity:
1. OSPF(routing protocol) use Mac.
2. PGP(email system) use digital signature.
2.1.1 Cryptographic Hash Functions : Ensure Message Not to be tampered
A crytographic hasn funciton should satisfy:
If x == y : H(x) = H(y)
x != y : H(x) != H(y)
同时, x (arbitraty length) —Hash Function—> H(x) (fixed length)
Example
SHA
Issue
仍无法确定发送方是否为发送方本身
Solution: MAC
2.1.2 Message Authentication Code (MAC) : Ensure the origin of message
双方拥有a shared secret : authentication key
MAC = H(message + authentication key)
发送方发送messgae + MAC
接收方接收, then check H(message + authentication key) ?= MAC
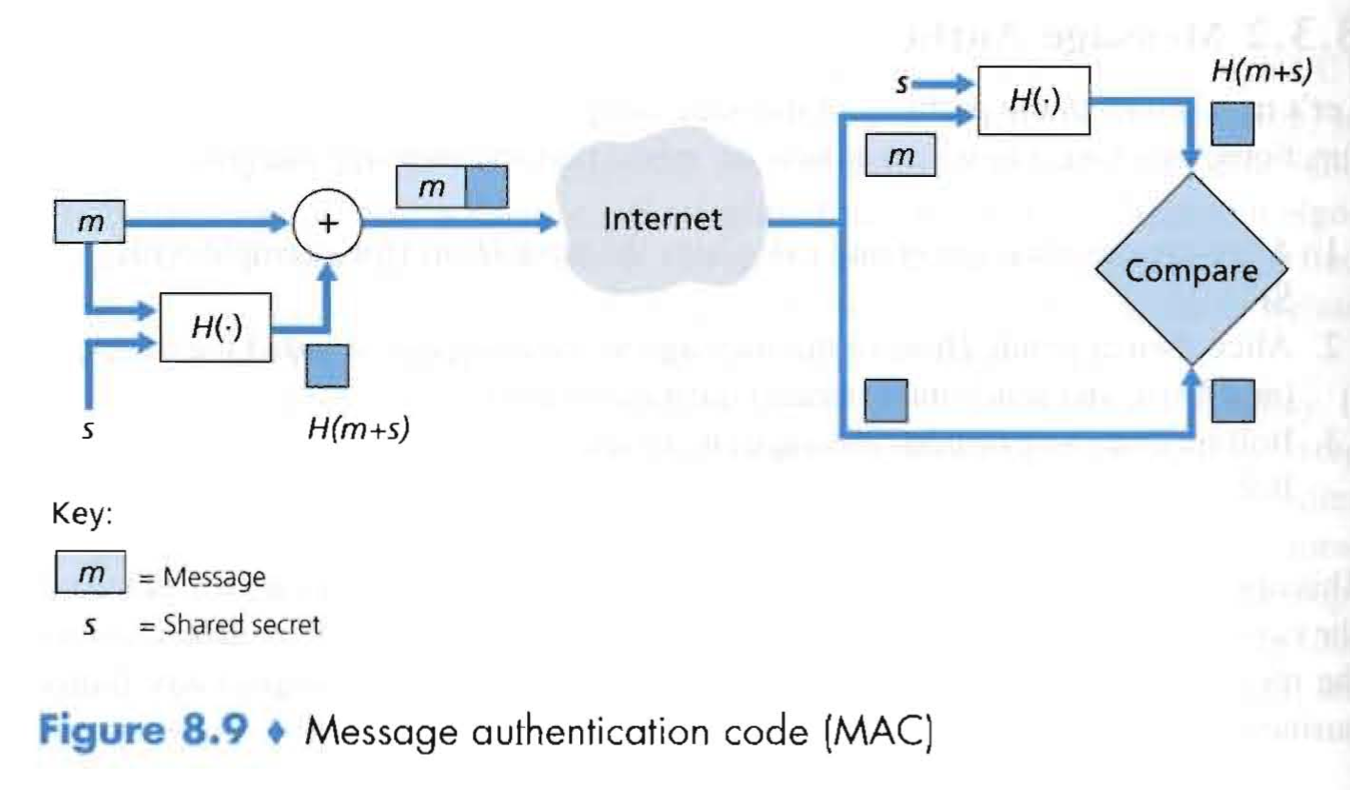 图片参考文献[1]
图片参考文献[1]
Issue
如何distribute the shared authentication key
Solution: + 加密然后发送
2.2 Digital Signature
证明某人签署了材料
思路:
必须附有something unique to the signer
Q: 可否采用MAC作为signature?
A: The answer is no. In this case, the key will be no more unique to the signer.
可采用public-key cryptography:
K+(K-(m)) = m
既保证了消息的origin, 也保证了消息not to be tampered. 可见 public-key cryptography满足了message integrity 的要求。
signature = K-(m)
Issue
- Expensive Computation
Solution: 引入hash functions
signature = K-(H(message)) (H(m) is of fixed-length, leading to less computation.)
发送方发送: message + signature.
接收方接收, then check H(message) ?= K+signature. - Whehther the public key belongs to the real owner?
Public Key Certificationcertifying that a public key belongs to a specified entity
Solution: Certification Authority (CA) 负责 把public key 和 entity 绑定 (1)创建一个certificate, 包含 public key 和 owner 独有的信息 (2) digitally sign the certificate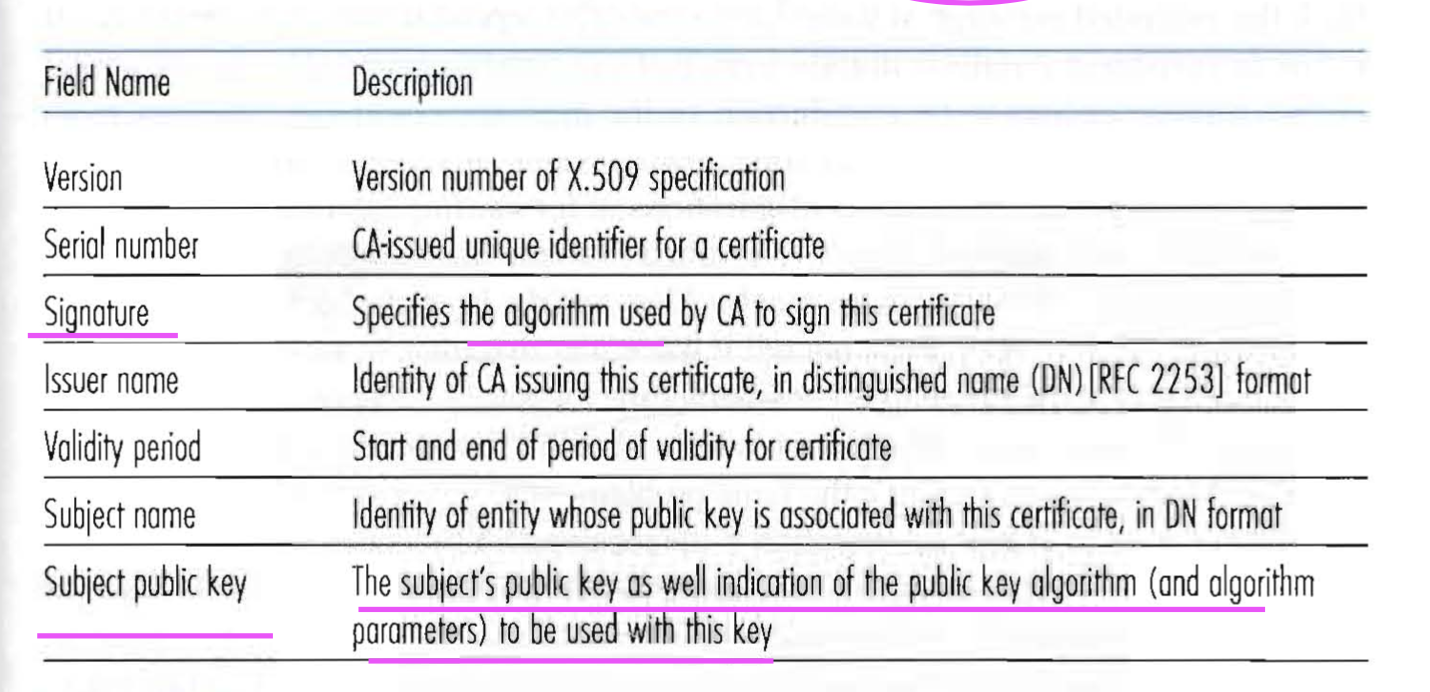 图片参考文献[1]
图片参考文献[1]
可见certificate里面包含了owner的public key, public key algorithm.
3. Network Attack
1. Playback Attack
solution : adding Nonces (which will never be used again)
MAC = H(message + authentication key + nonce)
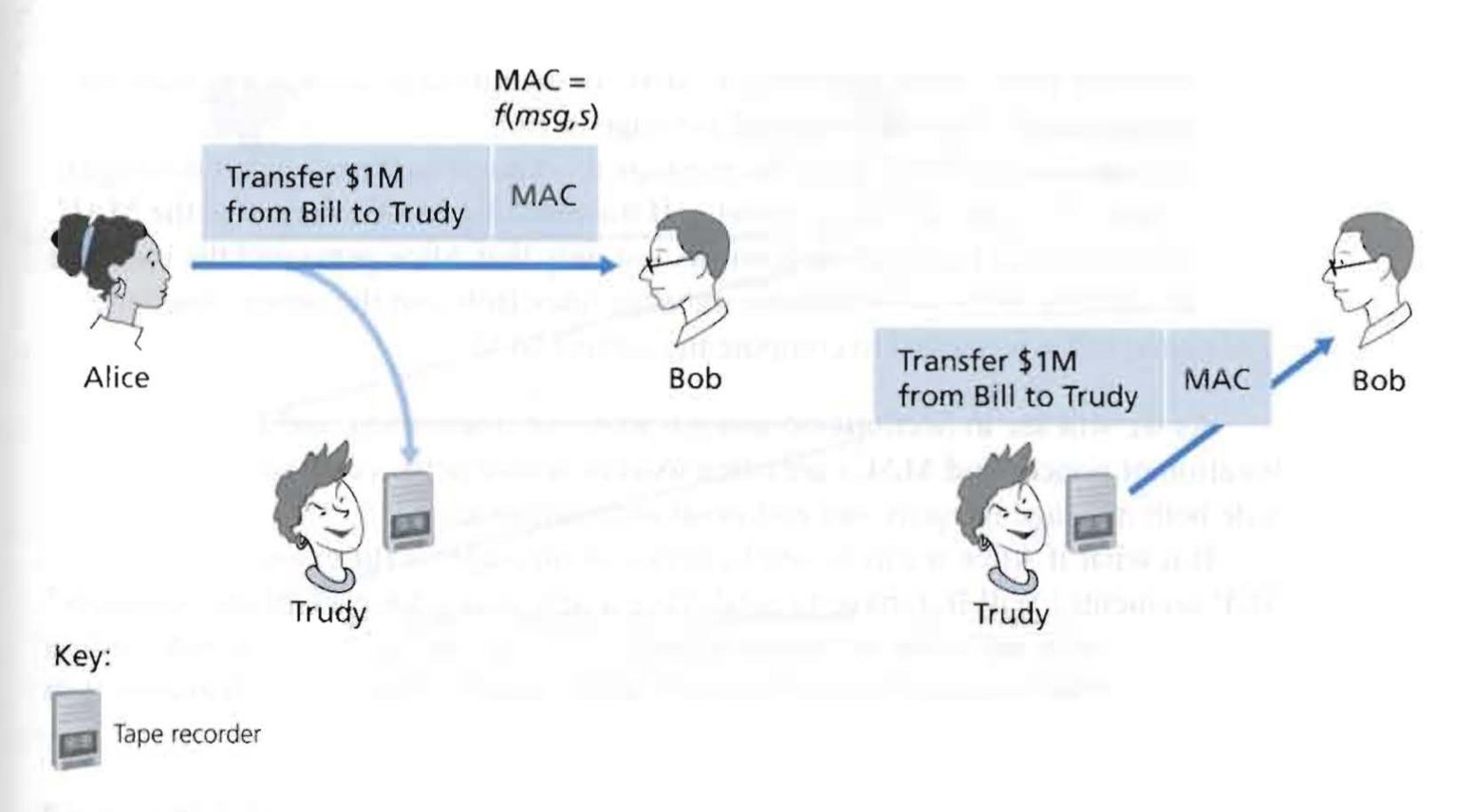 图片参考文献[1]
图片参考文献[1]
2. Man-in-the-middle Attack
solution : Public Key Certification
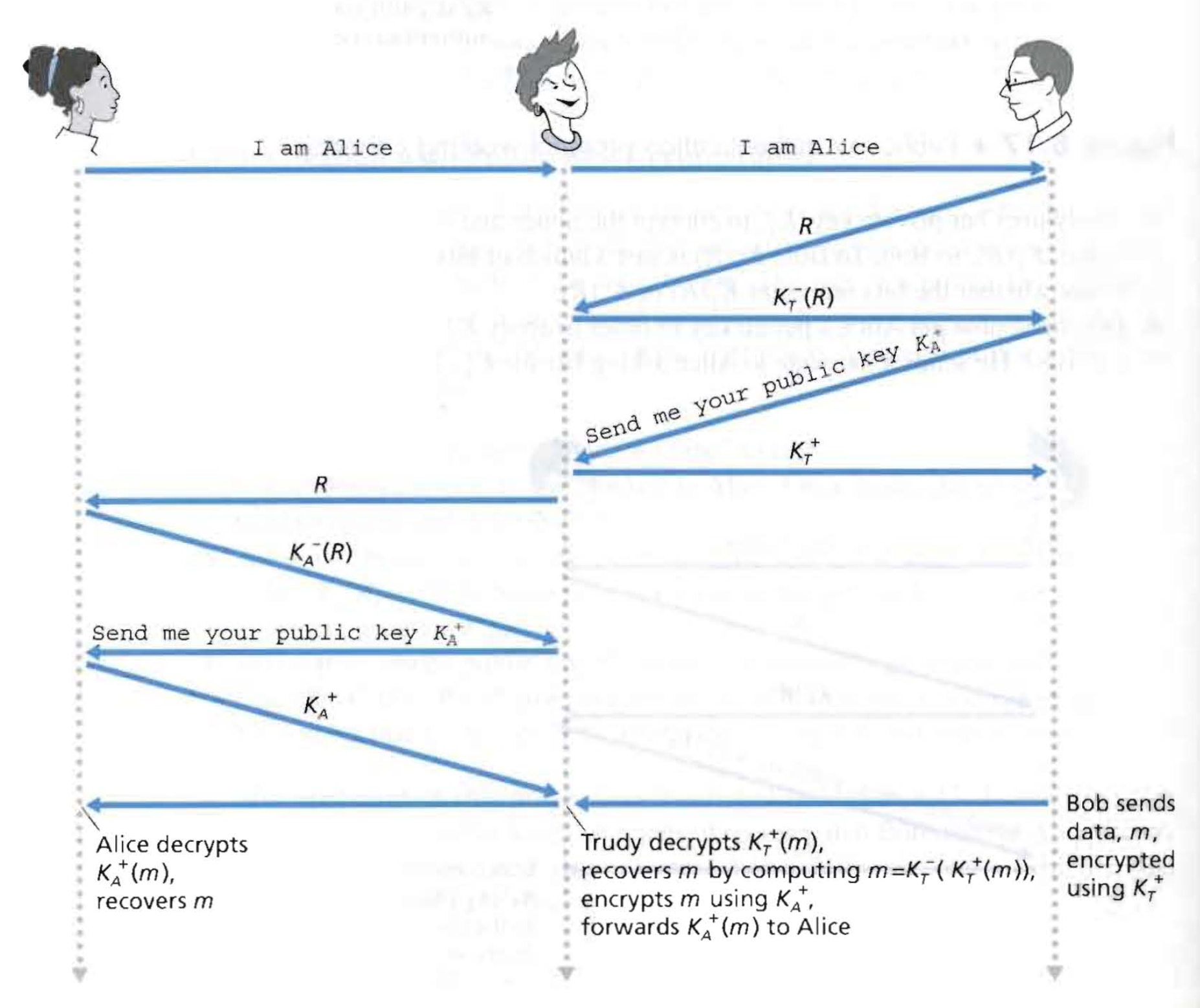 图片参考文献[1]
图片参考文献[1]
4.1 Case Study: securing email
Ripley —send messages to —– Zijun
Ripley:
(1) Ripley’s private key: KA-
(2) KS: symmetric key
(3) H: hash function
(4) KB : Zijun’s public key
public key : authentication
symmetric key: confidentiality
hash function: efficient computation
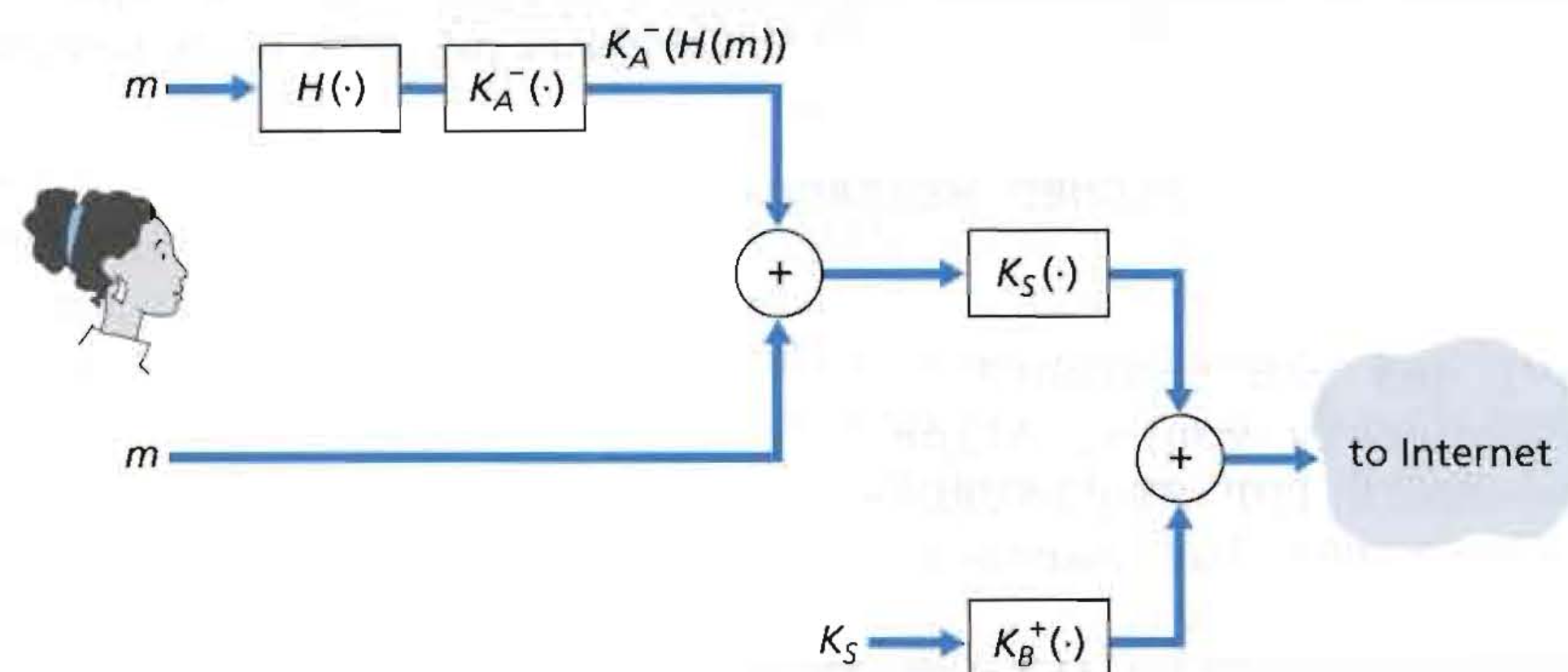 图片参考文献[1]
图片参考文献[1]
4.2 Case Study: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
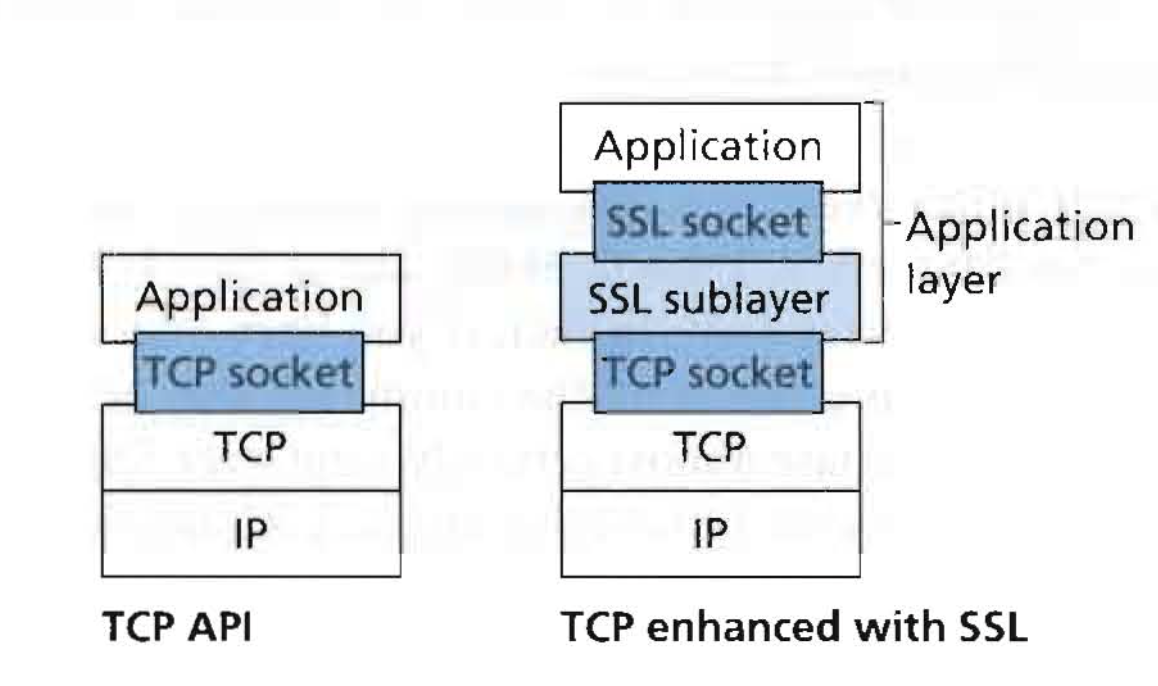
图片参考文献[1]
从程序员的角度,SSL跟TCP一样提供了各种socket API, 虽然SSL实际在应用层。
5. SSL Handshake

图片参考文献[2]
Explanation[3]:
1. client sends: A list of cryptographic algorithms + A client nonce (clear text)
2. server sends: choices including the symmetric algorithm, the public
key algorithm, the MAC algorithm + server nonce (clear text)
3. server sends: certficate
4. server sends: + Diffie-Hellman算法以及相关参数(服务端随机生成一个整数s,
计算pubkey_s = s * G),生成服务端pubkey,发送给客户端)
4. client verifies the certificate(public key解密 + 核对内容,
获得server public key), 此时客户端拥有 client_nonce, server_nonce
以及pubkey_s, 可以计算出PremasterSecret以及master key.
5. client sends: Diffie-Hellman算法以及相关参数(客户端随机生成一个整数c,
计算pubkey_c = c * G),生成客户端pubkey,发送给服务端)
6. 此时服务端拥有 client_nonce, server_nonce 以及pubkey_c, 可以计算出PremasterSecret以及master key.
7. client sends: MAC of all the handshake messages
8. server sends: MAC of all the handshake messages
服务端确定了密钥协商算法为“EC Diffie-Hellman”,发送给客户端。现在两端都知道了使用的是哪个曲线参数(椭圆曲线E、阶N、基点G)。
premaster secret 计算公式: 用于生成master secret 客户端:
PreMasterSecret:Q = pubkey_s * c = c(s * G)
服务端:
PreMasterSecret:Q = pubkey_c * s = s(c * G)
master secret 计算公式
MasterSecret = PRF(PreMasterSecret, “master secret”, Client.random || Server.random)
The MasterSecret will be sliced into 4 keys which known by both the server and client: encryption key AND Mac key for server and client respectively
session ticket
如果服务端想使用Ticket方式存储session状态,在Server Change Cipher Spec之前就需要发送New Session Ticket消息。
New Session Ticket方式与Session ID方式对比: SessionID方式,客户端在ClientHello的时候带着上一次SessionID过来, 服务端从自己内存中查找SessionID对应的session状态,并读取session状态快速恢复. SessionTicket方式,则是将session状态加密后,发送给客户端存储。 客户端在ClientHello时将SessionTicket带上,服务端就将其解密,读取出里面存储的session状态信息.
keys
(1)session key
(2)premaster key
(3)master key
参考
[1^] James F. Kurose and Keith W. Ross. 2012. Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (6th Edition) (6th. ed.). Pearson.
[2^] https://www.cnblogs.com/baihuitestsoftware/p/13151293.html
[3^] https://xz.aliyun.com/t/1039